The Engine for Brand Growth and Cost Optimization
I. Introduction: The Strategic Imperative of Process Design in the UAE
The United Arab Emirates, particularly Dubai and Abu Dhabi, is defined by its rapid pace of business, a commitment to global standards of quality, and a consumer base that demands premium, seamless experiences. In this dynamic landscape, a compelling brand strategy alone is insufficient; it must be flawlessly executed. Process and Workflow Design is the critical service that bridges the gap between ambitious brand promise and consistent operational delivery, making it the strategic engine for both brand growth and cost optimization.
This service involves the analysis, mapping, and redesign of an organization’s internal activities—from lead generation and creative content approval to customer service delivery and financial reporting—to achieve clarity, eliminate waste, and ensure every organizational action reinforces the brand’s core values. In the high-cost, high-competition environment of the UAE, optimized workflows are not merely about efficiency; they are the foundation for sustainable brand equity and competitive advantage.
II. The Dual Mandate: Brand Growth and Cost Optimization
The engagement of a Process & Workflow Design service is driven by two symbiotic goals, which are paramount to C-suite leaders in the GCC region:
A. Driving Brand Growth and Consistency
A brand is defined by the sum of its customer experiences. In a market where digital engagement is high, any inconsistency—a slow response, a misplaced document, a delay in service delivery—can instantly erode trust and brand value.
- Ensuring Brand Consistency: Optimized workflows create a standardized operating procedure (SOP) for every customer touchpoint. Whether a customer is dealing with sales, support, or marketing, a well-designed workflow ensures the brand voice, tone, and service quality are uniform. This consistent delivery is the bedrock of trust and brand loyalty.
- Accelerating Speed to Market: The UAE market moves quickly. Optimized workflows, especially in areas like creative content generation, legal review, and product launch protocols, drastically reduce cycle times. This agility allows the brand to capitalize on fleeting market opportunities, from seasonal campaigns to quick product iteration cycles.
- Enhancing Customer Experience (CX): A robust service design blueprint maps the entire customer journey, defining the Frontstage (customer-facing) and Backstage (internal support) activities. By removing friction in the backstage processes (e.g., automating data transfer between CRM and finance), the frontstage experience becomes seamless, fast, and personalized, directly boosting the brand’s reputation for excellence.
B. Achieving Significant Cost Optimization
In a region with high operational overheads, minimizing waste is crucial for profitability. Workflow design directly targets inefficiencies that drain resources.
- Reducing Operational Redundancy: Workflows eliminate unnecessary manual handoffs, data re-entry, and duplicated tasks. By automating rule-based, high-volume activities (e.g., invoice processing, lead qualification), businesses significantly lower labor costs and free up skilled employees for strategic, high-value work. Studies often show operational cost reductions of up to 70% in areas targeted for automation.
- Minimizing Errors and Rework: Manual, paper-based, or fragmented processes are inherently prone to human error. A single error in financial reporting, customer order fulfillment, or legal compliance can lead to costly rework, financial penalties, or reputational damage. Workflow automation enforces predefined rules and validation checks, leading to dramatic improvements in data accuracy (often by over 80%) and a direct reduction in the cost of quality assurance.
- Improving Resource Allocation and Scalability: By establishing clear metrics (KPIs) and process throughput, leadership gains visibility into where staff time and resources are truly being spent. This allows for optimized resource allocation. Furthermore, well-designed, digital workflows are inherently scalable. As a brand expands across the UAE or the wider GCC, the processes can handle increased volume without a proportional increase in headcount or infrastructure, making growth more cost-effective.
III. The Process & Workflow Design Methodology in the UAE
Consulting firms in the UAE typically follow a structured, multi-phase methodology tailored to the client’s strategic goals:
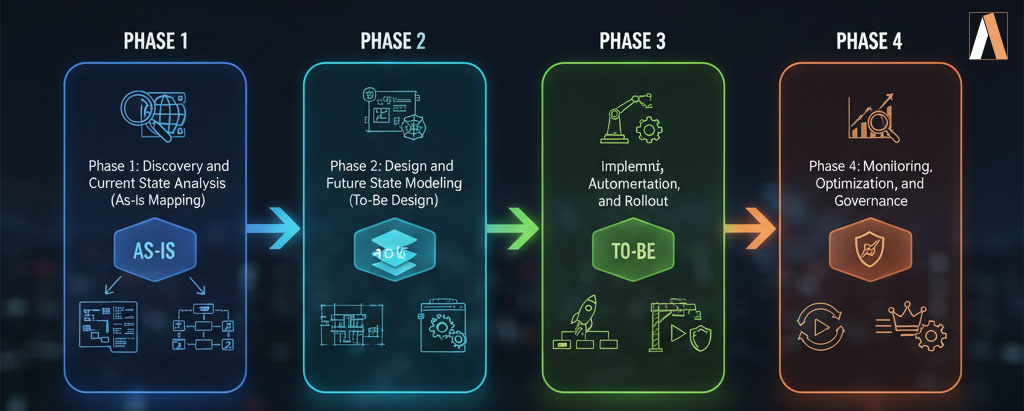
Phase 1: Discovery and Current State Analysis (As-Is Mapping)
- Goal: To establish a clear, documented baseline of existing operations.
- Activities: Consultants conduct interviews, shadow employees, and analyze existing documentation (forms, software logs). They create visual As-Is Process Maps (flowcharts) that highlight every step, role, and system involved.
- Key Deliverable: A detailed report identifying Pain Points, Bottlenecks, and Waste (e.g., unnecessary waiting time, redundant approvals), along with quantifiable baseline metrics (cycle time, error rate, cost per transaction).
Phase 2: Design and Future State Modeling (To-Be Design)
- Goal: To design optimized, future-state workflows that align with the brand’s strategic vision and cost targets.
- Activities: Consultants leverage best practices, benchmark against industry leaders in the UAE, and utilize Process Re-engineering (BPR) principles.
- Automation Strategy: Identifying all rule-based steps suitable for Robotic Process Automation (RPA) or specialized workflow software (e.g., CRM or HRIS modules).
- System Integration: Designing flows that connect disparate systems (e.g., linking the Marketing Automation Platform to the ERP system) to ensure seamless data flow.
- Organizational Design: Redefining roles and responsibilities to match the new workflow, focusing on cross-functional collaboration.
- Key Deliverable: To-Be Process Maps outlining the ideal, optimized flow, a detailed ROI Projection based on quantifiable savings, and a technology requirements document.
Phase 3: Implementation, Automation, and Rollout
- Goal: To deploy the new workflow design and supporting technology.
- Activities: This phase involves configuring or developing the chosen automation tools, integrating them with existing IT infrastructure, and running pilot programs.
- Training & Change Management: This is crucial in the UAE’s diverse workforce. Comprehensive training is provided to ensure user adoption and buy-in, emphasizing the “why”—how the new process benefits the brand and the employee.
- Pilot Testing: Launching the new workflow on a smaller scale to identify and fix unforeseen issues (bugs, user confusion) before a full, organization-wide rollout.
Phase 4: Monitoring, Optimization, and Governance
- Goal: To ensure long-term value capture and continuous improvement.
- Activities: Once deployed, the workflow is monitored using predefined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), such as completion time, adherence rate, and process error rate.
- Feedback Loops: Establishing a regular process for gathering user feedback and conducting periodic process audits.
- Continuous Improvement: Utilizing the collected data (Process Mining) to identify new opportunities for refinement and further automation, ensuring the brand remains agile in the ever-evolving UAE market.
IV. Critical Success Factors for UAE Implementation
To ensure the new processes drive both brand consistency and cost savings, UAE-based firms must adhere to key local best practices:
- Cultural Sensitivity and Multilingual Support: Workflows must account for the UAE’s diverse, multinational workforce. Documentation, training materials, and user interfaces should support both English and Arabic where appropriate to ensure clarity and user adoption.
- Alignment with Regulatory Compliance: The processes must be designed to adhere strictly to local regulations (e.g., VAT laws, data protection standards, and labor laws). Automation in the finance and HR departments must build in compliance checkpoints to mitigate risk.
- Focus on the Service Blueprint (CX): Given the UAE’s premium service culture, the workflow design must be rooted in the service blueprint. Every process decision should trace back to whether it enhances or detracts from the ultimate customer experience.
- Leadership Buy-in and Sponsorship: In the often-hierarchical corporate structures of the UAE, sustained C-level sponsorship is essential to overcome inter-departmental resistance and drive the necessary cultural shift toward process-driven consistency.
V. Conclusion
Process and Workflow Design is a transformative service for organizations in the UAE. It moves the conversation beyond theoretical brand positioning to the tangible, operational reality of service delivery. By enforcing consistency, accelerating time-to-market, and leveraging technology to eliminate waste, optimized workflows serve the dual purpose of:
- Strengthening the Brand: Creating the reliable, high-quality, and agile customer experience that the UAE market expects.
- Sustaining Profitability: Achieving quantifiable cost optimization through error reduction, labor savings, and improved resource utilization.
In a market where only the most agile, consistent, and efficient brands thrive, investing in professional Process & Workflow Design is no longer optional—it is the strategic necessity that future-proofs the organization for growth and dominance in the GCC region.